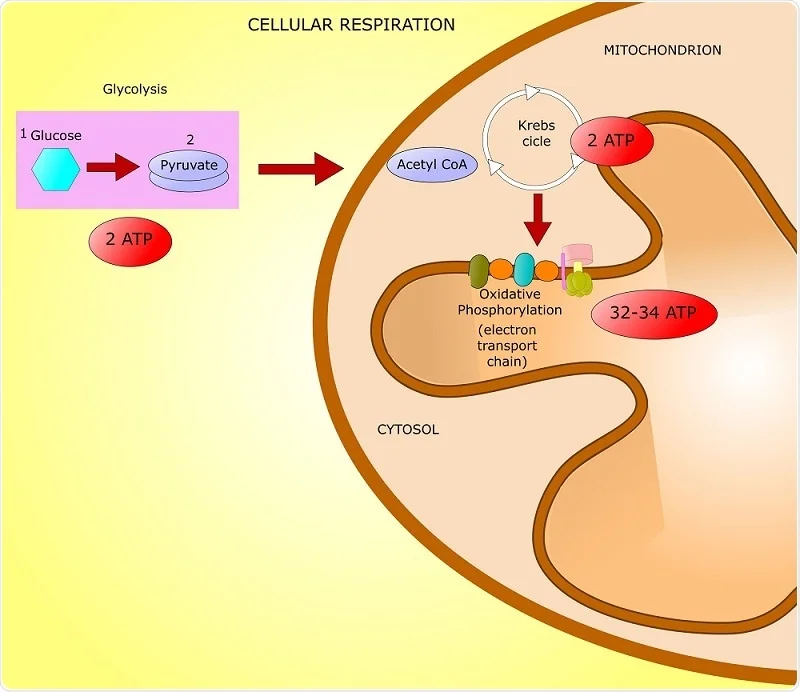
Prokaryotes produce 38 ATP per glucose molecule and eukaryotes produce 36 ATP why. Most prokaryotes are chemoheterotrophs.
In eukaryotes most cellular respiration reactions take place within the mitochondria.

HOW PROKARYOTES PRODUCE ATP. Eukaryotes have these organelles and cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria to convert nutrients into ATP the main energy storage unit for a cell. Prokaryotes also produce ATP but the enzymes required for its production are attached to the cellular membrane that surrounds the cell. In eukaryotic cells the theoretical maximum yield of ATP generated per glucose is 36 to 38 depending on how the 2 NADH generated in the cytoplasm during glycolysis enter the mitochondria and whether the resulting yield is.
Eukaryotes have these organelles and cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria to convert nutrients into ATP the main energy storage unit for a cell. Some researchers have suggested that mitochondria might actually be one of the reasons that. Professor Fritz Libmann and others discovered in 1956 that before amino acids can combine to form proteins they must be activated and this is achieved by combining with phosphate.
They play vital roles as decomposers and help recycle carbon and nitrogen. Through glycolysis citric acid cycle aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration and there are probably more. They live in a particular habitat because they are able to eat whatever is around them.
In this manner do prokaryotic cells produce ATP. Prokaryotes have their ATP synthesis machinery embedded in the cell membrane instead of of the mitochondrialthylakoid membrane which is the case for eukaryotes. Decarboxylation of pyruvate 4.
Many break down organic wastes and the remains of dead organisms. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms get the energy they need to grow and maintain normal cellular function through cellular respiration. For example there are bacteria and archaea that break down hydrogen sulfide to produce ATP.
How does prokaryotic cell produce ATP. Those bacteria that carry out aerobic respiration use an electron transport chain that pass. Elsewhere in the cytoplasm aminoacids are selected for activation.
Prokaryotes also produce ATP but the enzymes required for its production are attached to the cellular membrane that surrounds the cell. In eukaryotes the electrons released during glycolysis are carried by NADH and transferred to FAD to form FADH2 in order to get the electrons across the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. I know that the two are lost but I am not sure if it is in the processing of the sugars or the transport.
Because FADH2 results in the production of fewer ATPs than NADH there is a cost to the eukaryotic cell of getting the electrons into the mitochondrion. How Many Atp Do Prokaryotes Produce How Many ATP Do Prokaryotes Produce. Besides do prokaryotes produce ATP.
Prokaryotes have a wide range of metabolisms and this determines where they live. Prokaryotes lack mitochondria and instead produce their ATP on their cell surface membrane. Carbohydrates for ATP Production Besides glucose other monosaccharides as well as disaccharides and polysaccharides can be used to produce ATP.
In prokaryotes they occur in. Total Theoretical Maximum Number of ATP Generated per Glucose in Prokaryotes 38 ATP. Sucrose for example is first digested by the enzyme sucrase into its two monosaccharides glucose and fructose.
What reaction phase of respiration produces no ATP molecules. The phases in bold below do not produce any ATP directly. 34 from oxidative phosphorylation.
Most prokaryotes generate 38 ATPs from one glucose molecule. Cellular respiration occurs in all cells. Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Theoretically in prokaryotes we get 38 ATPs from per glucose molecule 4 from substrate-level phosphorylati View the full answer. 4 from substrate-level phosphorylation.
Cells constantly need a supply of ATP so cells are continuously carrying out. Eukaryotes with most of their energy by producing energy-rich molecules called ATP. Biology textbooks often state that 38 ATP molecules can be made per oxidised glucose molecule during cellular respiration 2 from glycolysis 2 from.
It is the process through which the cell breaks down glucose to produce ATP. Prokaryotes such as anaerobic bacteria rely heavily on the first stages of glucose break down - deriving enough energy from the breaking and restructuring of chemical bonds to make 2 ATPs per glucose. The activation involves the reaction between aminoacid and ATP.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Prokaryotes also produce ATP but the enzymes required for its production are attached to the cellular membrane that surrounds the cell. They depend on other organisms for both energy and carbon.
Does anyone know where these two are lost or why. Electron transport chain 6.

Difference Between Cytoplasm And Cytoskeleton Definition Structure Function Similarities Basic Anatomy And Physiology Study Biology Biochemistry Notes
Re How Do Bacteria Produce Energy Without A Mitochondrion
Re How Do Bacteria Produce Energy Without A Mitochondrion

How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora

Cellular Respiration Microbiology
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora

How Much Atp Is Produced In A Prokaryotic Cell In A Krebs Cycle And Etc Quora
What Process Produces Most Atp In Eukaryote Cells Quora

Mitochondria The Electrochemical Proton Gradient And Atp Synthase Mitochondria Learning Science Medical Textbooks
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora

Aerobic Vs Anaerobic Respiration Venn Diagram Cellular Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Atp Synthesis In Prokaryotes Youtube

Cellular Respiration Biology Classroom Biochemistry Teaching Biology

Role Of Mitochondria In Cell Mitochondria Science Cells Mitochondrial Disease